Although by now the Internet is full of information about Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, there are so many diverging opinions on the subject, it’s good to address some of the essentials right here. While the perspective presented in this post is just one of many, it can be considered a simplified, although incomplete, quick start for newcomers.
The explanations given should require little or no technical knowledge in advance. They are intended as a high-level intro that necessarily skips many topics to cover most of the important basics that sooner or later everyone should know. The estimated time to read all of this information is less than 5 minutes.
Even after you’ve gone through it all, it is important to emphasize that the best way to learn is by doing and by getting out from behind the computer and meeting people in person at various events, rather than getting random web sites and chat rooms. That said, the presentations given by Andreas M. Antonopoulos are generally very highly recommended, and you can also learn a lot from watching the videos and reading the other posts on this site.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the world’s first fully decentralized digital currency, or cryptocurrency. Unlike government-issued money like euros or dollars, bitcoins do not have physical form in coins and notes, but are represented virtually as balances on the global Bitcoin network.
This network knows no borders and is decentralized in that it is not controlled by a single central authority like a government or bank. It has a fixed supply of 21 million bitcoins, which is intended to be impossible to change due to the algorithm included in its software. It is arguably the best known, most accepted, proven, tested, stable and secure of all of the thousands of similar or related solutions that have come on the market since it was launched in early 2009.
How does Bitcoin work?
The Bitcoin network is a peer-to-peer system in which anyone using the correct hardware and software can participate. For this reason it is said to be permissionless, in the sense that there is no third party who can exclude anyone else from connecting to the network and using the software. There is no bank or other company that can block or shut down your account or prevent you from receiving a valid transaction.
This open and permissionless characteristic is one of the central tenets of the system. In sharp contrast to what critics have said about Bitcoin, the fact that “a terrorist may be secretly running a Bitcoin node” does not make it more unsafe. The system is actually more safer the more full nodes are running since these independent computers are verifying transactions and making sure all of the balances held by each person are always correct.
The permissionless network allows us to make a transaction — in essence to transfer a certain amount in Bitcoin — in such a way that the same coins you transfer cannot be spent twice by you or anyone else. Compare that to sending a digital photo on the Internet where you or the recipient could easily make multiple copies of the same digital image and simultaneously transfer it to many other people. One of the features that made Bitcoin revolutionary was that the network allows digital information to be transferred but prevents the coins spent in one transaction from being simultaneously spent in any other. That special ability requires a permissionless network because with a closed number of participants there is a very high risk of collusion that would allow the system to be gamed in various ways. Regulator-friendly cryptocurrencies tend to suffer from this weakness; a limited number of nodes or validators that puts control into a smaller group that the users would have to trust.
What is a Bitcoin wallet?
A Bitcoin wallet is software that allows a user to store, send and receive the digital tokens called bitcoins. The wallets for most cryptocurrencies work in a similar way, and a lot of the wallet software currently available can store many different coins simultaneously. The most important aspect of maintaining a wallet is protecting the password or private key. This information is highly sensitive and cannot be recovered by anyone. Pamela Morgan gave one of the best presentations for users on wallet security, that is great for both beginners and more experienced users, during Bitcoin Wednesday on 19 October 2016.
What are Alts?
There are now thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies, known as alt-coins or alts, because it is clear that the world will never agree on just one. Most are in some way or another copycats with sometimes only very minor changes in the implementation. But some are highly original that intend to offer improvements or address uses that Bitcoin has not yet covered.
What are Bitcoin maximalists?
Bitcoin maximalists are those who believe — to a greater or lesser extent — that Bitcoin is (and should be considered) the one true cryptocurrency to rule them all, and that pretty much everything else that came later is inferior. At its extreme, a maximalist position is a kind of radical fundamentalism that views (practically) all alt-coins as inferior, and leaves almost no room for other projects.
While there is obviously a lot of valid criticism of alt-coins, Bitcoin also is highly experimental and not above critique. Bitcoin itself is an alternative to the traditional financial system, and the very nature of this kind of disruptive innovation (arguably all innovation) is that it emerges when the existing solutions do not meet all of the world’s needs.
Most maximalists will therefore concede that the introduction of alt-coins is part of the Bitcoin governance model in the sense that anyone is free at any time to suggest changes to the way the network works. These changes can be made in the following ways:
- Through Bitcoin Improvement Proposals, design documents evaluated by the Bitcoin community and introduced when there is enough consensus;
- By starting a new project which may or may not involve copying or adapting some aspects of the original Bitcoin software; or
- Through the introduction of changes directly into the existing software, even without the required consensus, which would cause the Bitcoin network split, through the phenomenon known as a fork. Two most notable examples are Bitcoin Cash, a fork of Bitcoin, and Ethereum Classic, which is a fork of Ethereum.
Why Should I Invest in Bitcoin or Other Cryptocurrencies?
An investment is a highly sensitive, multi-factorial and personal decision, and for this reason it’s probably a bad idea to take this type of advice indescriminately from people you just met on the Internet. Someone who dispenses investment advice in an official capacity, especially if he or she is promising guaranteed returns, may even be breaking the law. The fact is that cryptocurrency prices are extremely volatile, and therefore highly risky financial investments. Bitcoin’s limited supply of 21 million creates a scarcity that some have compared to gold, but unlike that precious metal its value depends on the work of specialized software engineers so thinking about it as a highly speculative early stage tech stock might be more accurate. As of mid-2018, cryptocurrency projects do not have a higher failure rate than early stage tech investments.
What Are Some Tips and Strategies for Cryptocurrencies?
A safer way to view cryptocurrency is not like an investment at all, but as a technology of the future that can already be used today. Therefore, while investing can be a complicated, personal decision, the opportunity to sell goods or services in exchange for bitcoins is invaluable, and can be done without hesitation, even if you decide to exchange all or some of the amount you receive immediately back into traditional fiat money. Using cryptocurrency is the best approach to learning about it and preparing yourself to live in the future. A good, basic rule of thumb to observe in buying a new crypto-asset is to make sure you understand what the uses are for the new token and to carefully decide whether you would like to participate in the project as a user, rather than an investor. A cryptocurrency trader who strongly believes he needs to remain emotionally unattached from his investments might do better participating in projects that address financial applications. Currently only about 20-25% of the projects launched between January 2017 and July 2018 (representing a $12 billion-dollar ICO market) are financial ones.
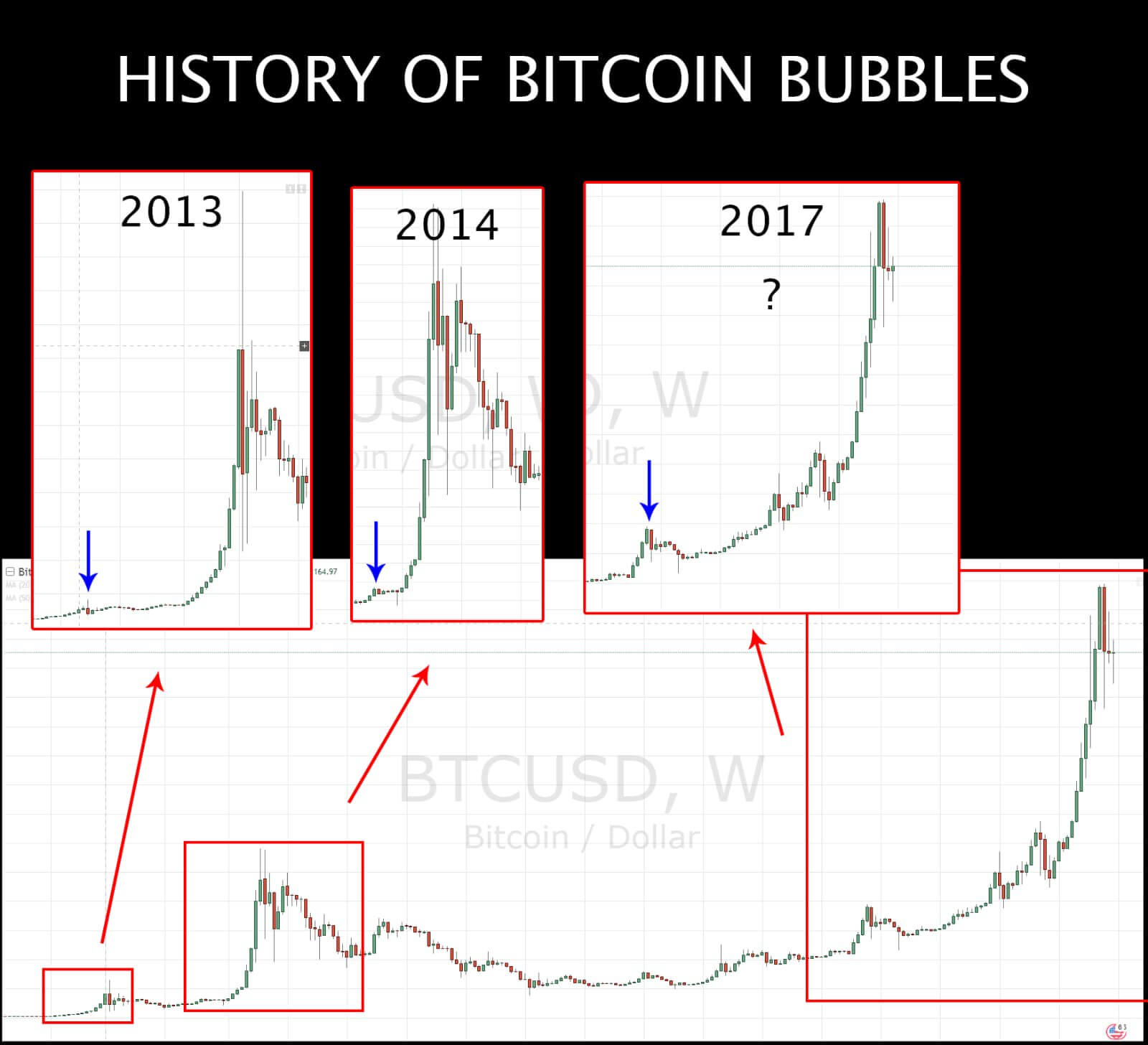
Is Bitcoin in a bubble?
The definition of “bubble” is poorly defined and highly subjective. It depends a great deal on your investment horizon and the sentiment of whoever is answering the question, as the graphic below clearly illustrates.
What is the ideology behind Bitcoin?
Sustainability through governance of common pool resources by a community of its users rather than a central authority. In 2009, the year that Bitcoin was launched, the Nobel prize in economics was awarded to a woman for the first and only time. Her name was Elinor Ostrom. Her work involved a collection of principles for solving what’s known as tragedy of the commons problems — i.e. preventing the over-exploitation of shared and limited resources. It seems as if Bitcoin may have been one of the first global, technical implementations of her ideas.